A Holistic Overview of the Interconnected Global Optical Transport Network Industry
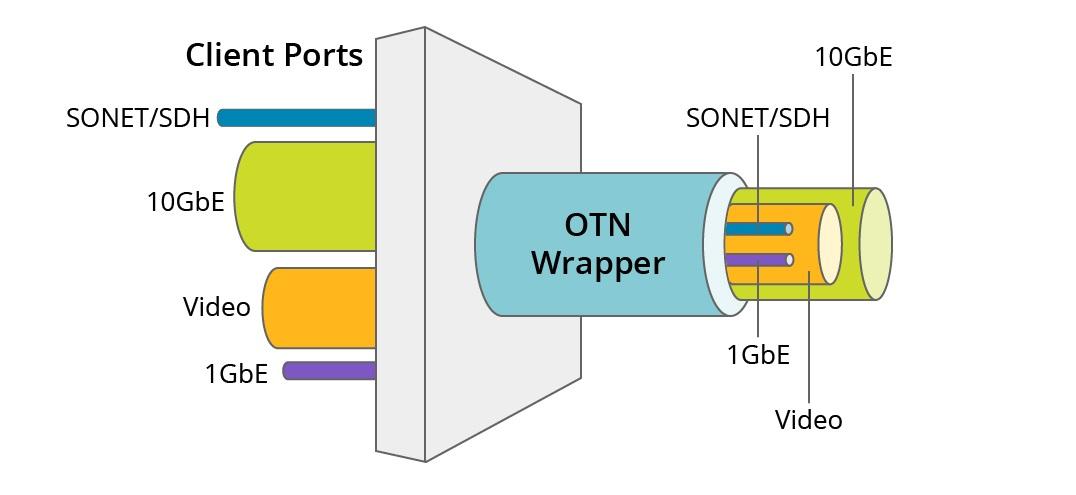
The global Optical Transport Network industry is a highly sophisticated and deeply interconnected ecosystem of companies that collectively design, manufacture, and deploy the foundational infrastructure of the internet. This industry is responsible for the high-speed pathways that carry nearly all long-distance digital communications, making it a critical enabler of the modern global economy. Its health and innovation are directly linked to our ability to support future technological advancements, from AI to the metaverse. The systemic importance of this sector is reflected in its strong and stable growth, with projections indicating the industry will achieve a market value of USD 34.46 billion by 2032, advancing at a consistent CAGR of 7.43% during the 2024-2032 period.
The industry's supply chain is multi-layered and highly specialized. At the base are the manufacturers of fundamental optical components and semiconductor chips. Companies like Lumentum, Coherent Corp., and Marvell produce the essential building blocks, such as lasers, photodetectors, modulators, and the powerful coherent Digital Signal Processor (DSP) chips. These components are then sold to subsystem manufacturers who assemble them into modules like transponders and pluggable transceivers. Finally, the major system vendors—Ciena, Nokia, Infinera, and others—integrate these subsystems with their own hardware and software to create the complete, end-to-end OTN platforms that are sold to network operators. The health of this entire supply chain, from raw materials to finished systems, is crucial for the industry's stability and progress.
The key stakeholders in the industry are a diverse group with varied interests. The equipment vendors are focused on technological innovation and market share. Their customers, the network operators—which include telecom companies (AT&T, Verizon), cable operators (Comcast, Liberty Global), and the massive hyperscalers (Google, Meta)—are focused on deploying this technology to meet customer demand in a cost-effective and reliable manner. Other important stakeholders include the various standards bodies, such as the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), which ensure interoperability between different vendors' equipment. Government and regulatory bodies also play a significant role by influencing policy, spectrum allocation, and national security considerations related to critical communication infrastructure.
The OTN industry faces a continuous set of challenges and opportunities that shape its direction. A major challenge is the immense cost of research and development required to keep pushing the boundaries of optical physics and engineering to achieve higher speeds and greater efficiency. Supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions can also significantly impact production and deployment schedules. On the other hand, the industry is presented with massive opportunities. The rise of edge computing is creating a new demand for high-capacity metro and regional networks. The explosion of data traffic generated by artificial intelligence and machine learning workloads requires an even more robust and scalable transport layer. These forces ensure that the optical transport industry will remain a dynamic and essential field of innovation for decades to come.
Explore Our Latest Trending Reports:
GCC Intelligent Document Processing Market
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness